What is a VMware Snapshot?
VMware snapshots are a quick and easy way to back up the state of a virtual machine (VM) before testing a patch, software update, or other change. A VMware snapshot preserves the current state and data of the VM, so that when testing is complete, you can quickly restore the VM to the desired state.
You can create a snapshot file with or without memory. An in-memory snapshot also captures the VM's memory state and power settings. If you create a memoryless snapshot and restore to that snapshot, you will need to start the VM manually.
To be able to gracefully shut down the guest file system, VMware tools must be installed on the virtual machine. The graceful shutdown function purges dirty buffers from the operating system's in-memory cache to disk.
Snapshots are not intended to be used as a fallback strategy.
What files are created when I create a snapshot?
When you create a snapshot, the operation triggers the creation of files:
- .vmdk file – Machine file to which the guest operating system can write.
- -delta.vmdk – A delta disk (also called a child disk) is the difference between the current state of the virtual disk and the state that existed when the previous snapshot was created. The delta disk is made up of two files: a small descriptive file and a file that contains raw data. The descriptive file and the raw data file are also called “redo logs”.
- .vmsn file – Optional file that saves VM memory. As explained earlier, if you do not capture the memory state, the restore-to-snapshot operation will interrupt the execution of the virtual machine, which will have to be restarted manually.
- .vmsd file – Database file containing information about VM snapshots and all relationships between snapshots and between delta disks for each snapshot.
How to manage VMware snapshots?
You can use the vSphere Web Client to grab new snapshots, delete snapshots, and more. The options are:
- Create Snapshot – Creates a new snapshot of a virtual machine, which becomes the current snapshot. You can create a snapshot when a virtual machine is powered on, powered off, or suspended.
- Remove Snapshot – Removes a snapshot and any associated storage.
- Remove All Snapshots – Removes all snapshots associated with a virtual machine. If there is no snapshot for the virtual machine, this operation simply returns success.
- Revert to Snapshot – Changes the running state of a virtual machine to the state of the selected snapshot. This option is the same as the vSphere/VI Client Snapshot Manager Go To option.
- Revert to Latest Snapshot – Reverts the state to the most recent snapshot of the VM.
- Consolidate – Merges the redo log tree. This feature is supported in vSphere 5.0 and later.
How do I create a snapshot?
1. Access the VMware vSphere Snapshot Manager by right-clicking a VM and then clicking Create Snapshot . You can also select VM > Actions > Snapshots > Take snapshot .
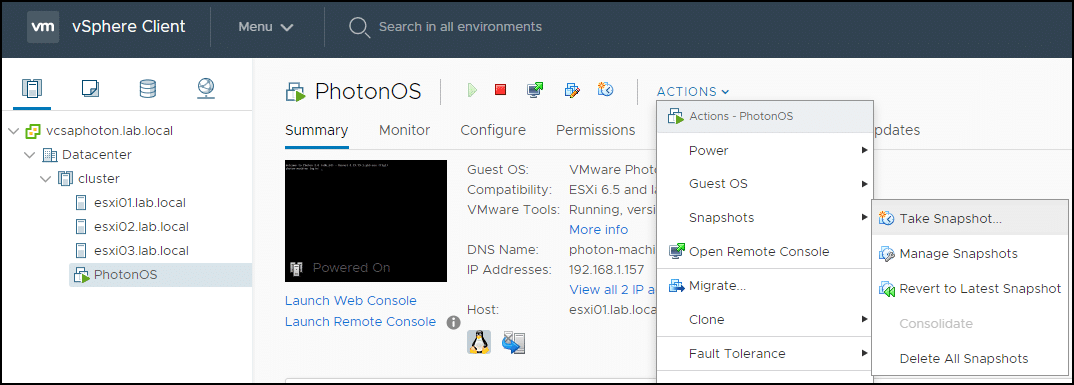
2. In the pop-up window, enter a name and description for the snapshot. We recommend including a detailed description of the operations performed on the VM or the configuration of the VM.
3. If you check the “Snapshot the virtual machine's memory” option, the snapshot will also save the VM's memory. If you check this box and the VM is running when you take a snapshot, the snapshot icon will be green.
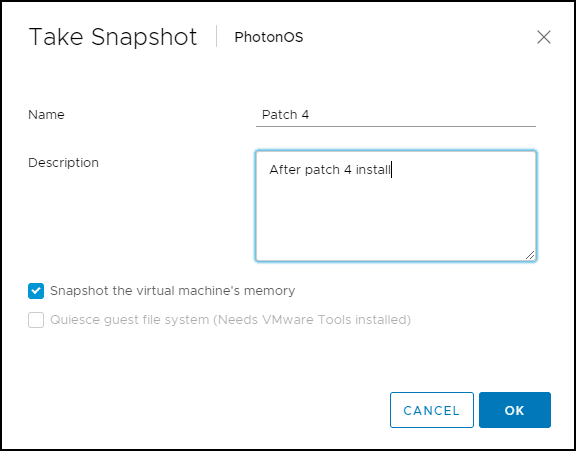
4. Click OK to create the snapshot.
How do I restore to a snapshot?
The figure below shows several snapshots to choose from. By restoring to a snapshot with a green icon, the VM will be running.
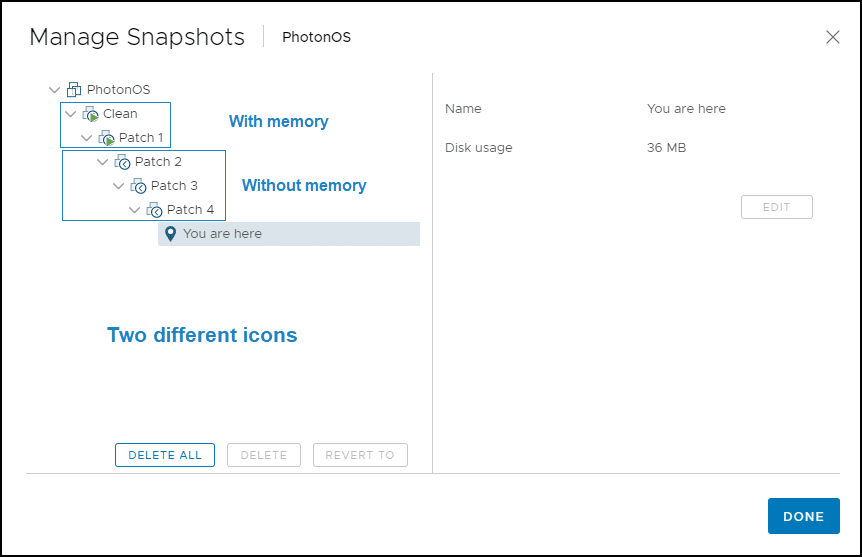
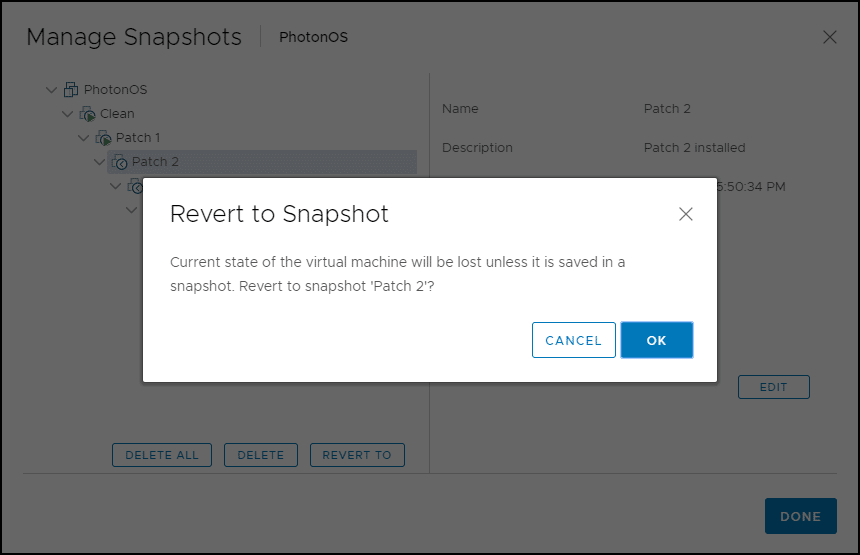
1. To restore to a snapshot, select one of the snapshots (eg Patch 2) in the Snapshot Manager and click Revert To .
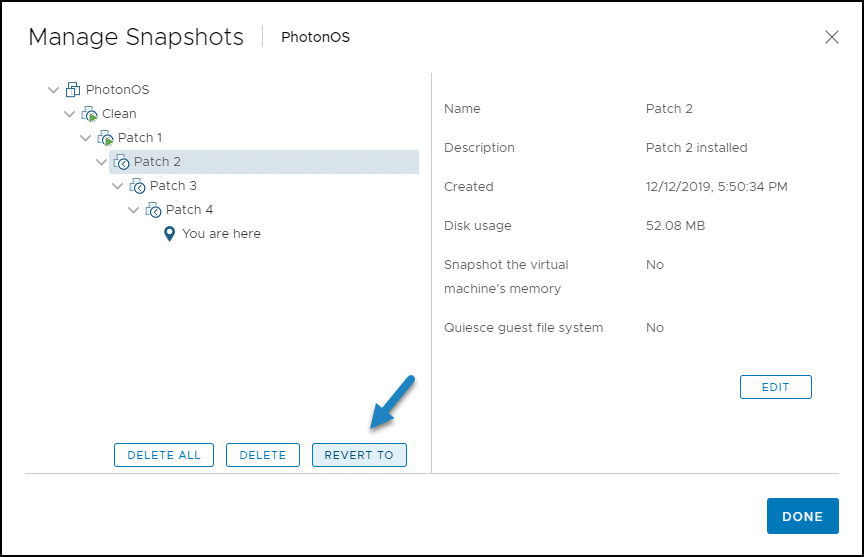
2. Click OK.
3. A message is displayed indicating that the current state of the virtual machine will be lost if it is not saved in a snapshot. This means that if you made changes to the VM, but did not back them up by creating a snapshot, your work will be lost. If you want to continue, click OK .
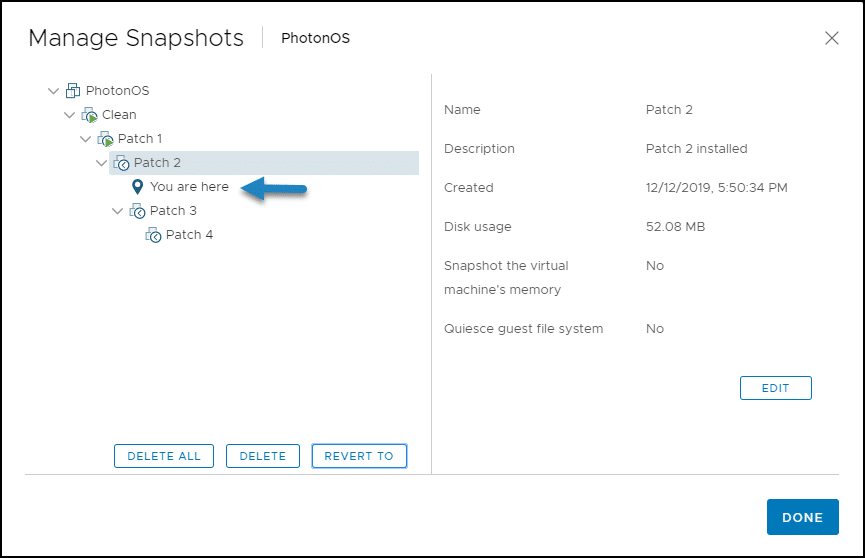
4. The snapshot manager screen shows you where you are in the snapshot tree. Click OK. As the Patch 2 snapshot does not include machine memory, you will need to start the VM manually.
Best Practices for Managing VMware Snapshots
VM snapshots take up a lot of space, so it's best to limit yourself to 2 or 3 of them.
Snapshots can be used on test or development VMs, but not on production VMs. A VM with snapshots typically performs poorly because you double the IOPS, and the CPU is overloaded when calculating the block-level difference. Performance degradation depends on how long the snapshot or snapshot tree has existed, how deep the tree is, and how much the VM and its guest OS have been modified since creation of the snapshot.
As stated earlier, snapshots are not meant to be a backup and recovery method. Always use appropriate backup software for your data center.
Snapshot Manager can only detect snapshots for individual VMs. Third-party solutions are available to view and manage snapshots of multiple virtual machines, providing greater control over the virtual environment. For example, you can quickly spot and investigate the unauthorized creation or deletion of snapshots in your virtual environment.
Conclusion
Snapshots are an interesting virtualization technology, but use them sparingly and with caution. Keep in mind that if you store sensitive or regulated information on your virtual machines, you must manage your snapshots appropriately to avoid security and compliance issues.